Protected: Newsletter: 09/07/2015
Star formation in the outer regions of the early-type galaxy NGC 4203

NGC 4203 is a nearby early-type galaxy surrounded by a very large, low-column-density H I disc. In this paper, we study the star formation efficiency in the gas disc of NGC 4203 by using the UV, deep optical imaging and infrared data.
Applying galactic archeology to massive galaxies using deep imaging surveys

Various programs aimed at exploring the still largely unknown low surface brightness Universe with deep imaging optical surveys have recently started. They open a new window for studies of galaxy evolution, pushing the technique of galactic archeology outside the Local Group (LG).
Continue reading “Applying galactic archeology to massive galaxies using deep imaging surveys”Protected: Report to SAC: may 2015
The stellar accretion origin of stellar population gradients in massive galaxies at large radii
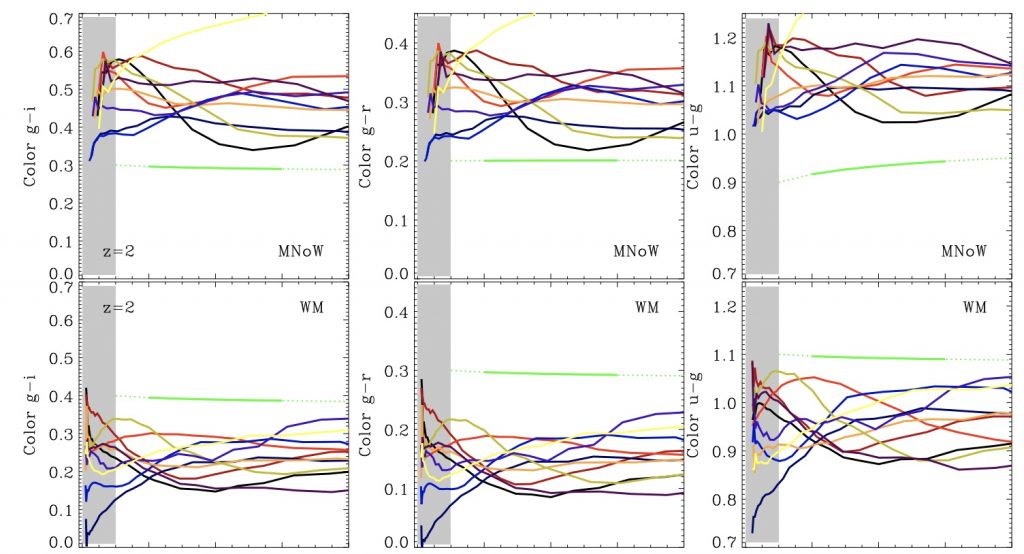
We investigate the evolution of stellar population gradients from z = 2 to 0 in massive galaxies at large radii (r > 2Reff) using 10 cosmological zoom simulations of haloes with 6 × 1012 M⊙ < Mhalo < 2 × 1013 M⊙. The simulations follow metal cooling and enrichment from SNII, SNIa and asymptotic giant branch winds. We explore the differential impact of an empirical model for galactic winds that reproduces the mass-metallicity relation and its evolution with redshift.
Continue reading “The stellar accretion origin of stellar population gradients in massive galaxies at large radii”Protected: Newsletter: 07/01/2015
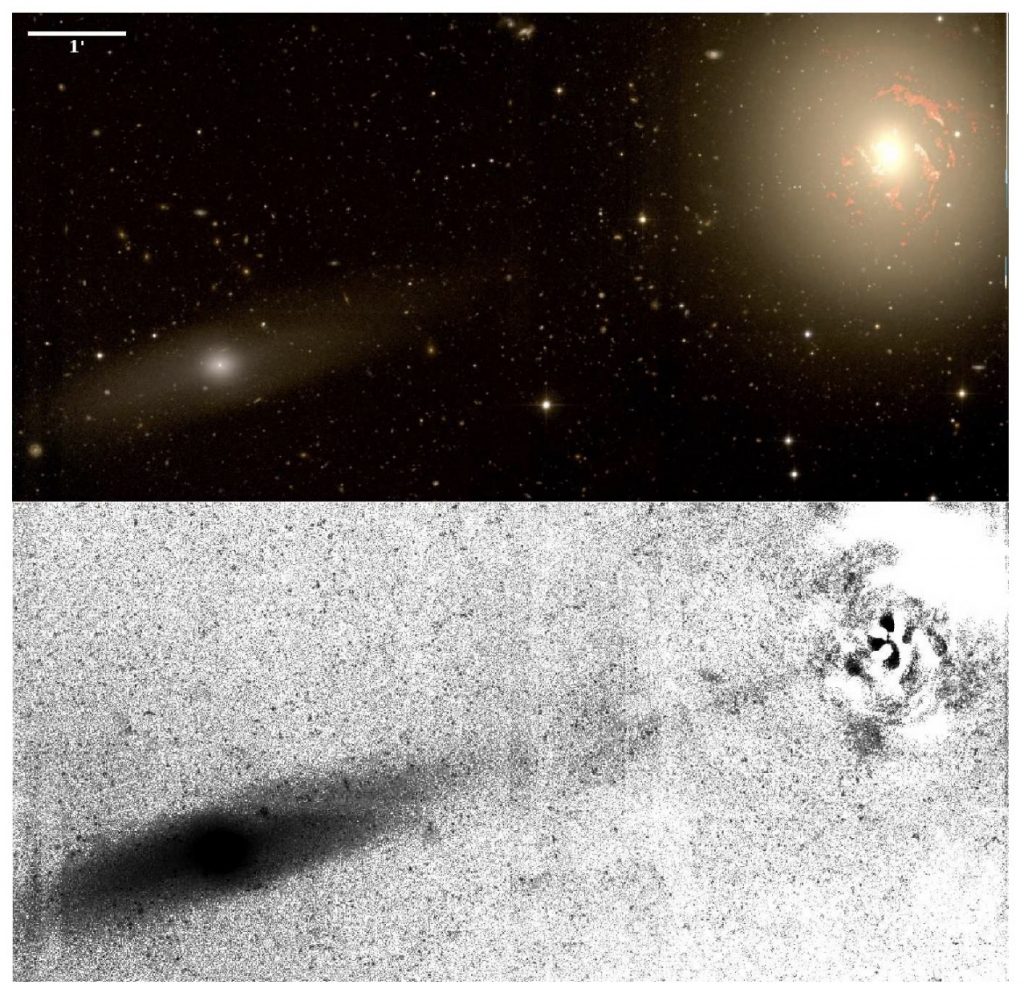
The new look of early-type galaxies and surrounding fields disclosed by extremely deep optical images
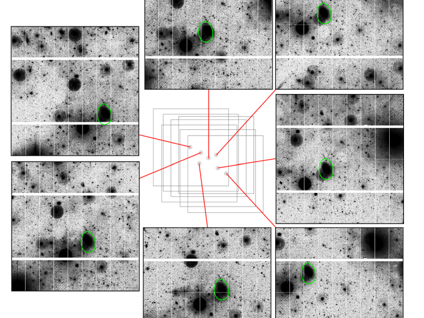
Galactic archaeology based on star counts is instrumental to reconstruct the past mass assembly of Local Group galaxies. The development of new observing techniques and data reduction, coupled with the use of sensitive large field of view cameras, now allows us to pursue this technique in more distant galaxies exploiting their diffuse low surface brightness (LSB) light. As part of the ATLAS3D project, we have obtained with the MegaCam camera at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope extremely deep, multiband images of nearby early-type galaxies (ETGs).
Continue reading “The new look of early-type galaxies and surrounding fields disclosed by extremely deep optical images”Accretion-Inhibited Star Formation in the Warm Molecular Disk of the Green-valley Elliptical Galaxy NGC 3226?
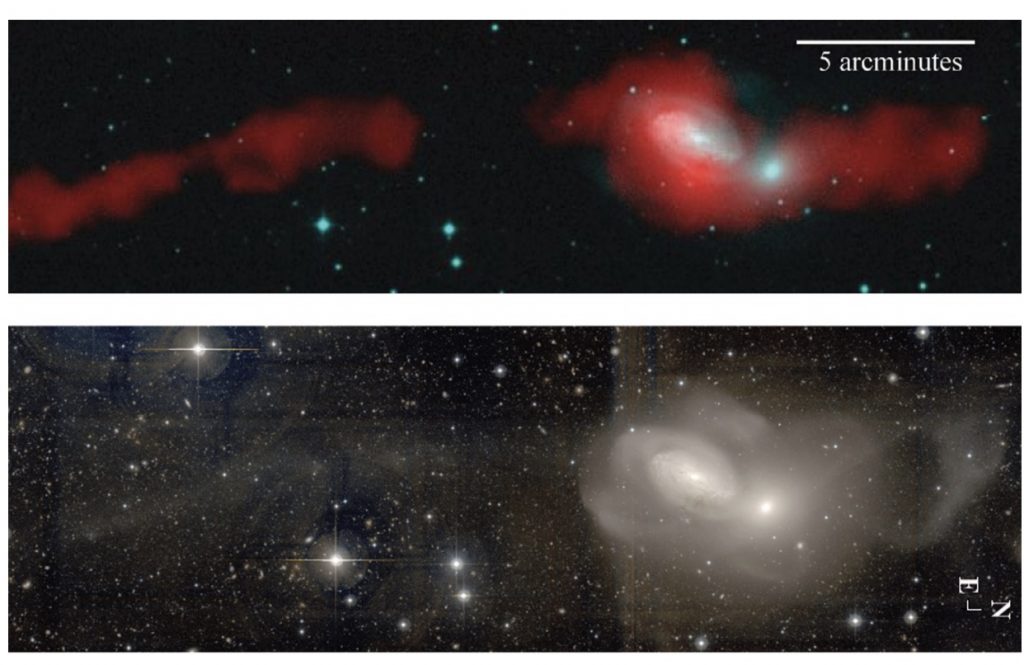

We present archival Spitzer photometry and spectroscopy and Herschel photometry of the peculiar “Green Valley” elliptical galaxy NGC 3226. The galaxy, which contains a low-luminosity active galactic nucleus (AGN), forms a pair with NGC 3227 and is shown to lie in a complex web of stellar and H I filaments.
Continue reading “Accretion-Inhibited Star Formation in the Warm Molecular Disk of the Green-valley Elliptical Galaxy NGC 3226?”Group image release 1 (as part of Atlas3D)
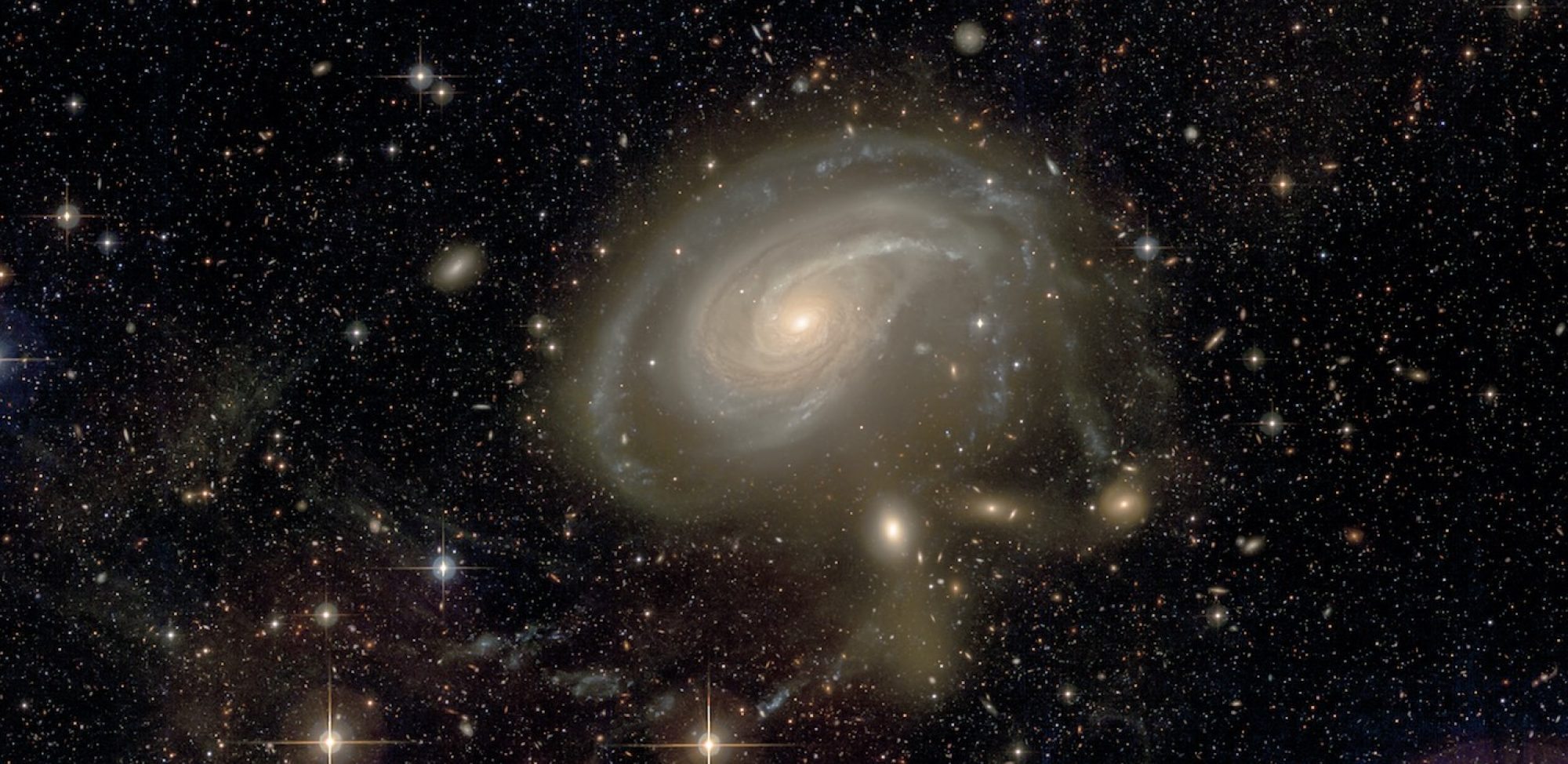
A sample of 92 galaxies with available deep g and r images (all located outside the Virgo cluster) presented in the Atlas3D paper XXIX: Duc et al., 2014. Images were obtained as part of of a series of regular multi–semester PI and snapshot programs in the framework of the ATLAS3D project (serving as a pilot program for MATLAS). The galaxies presented in this image release were observed between 2010 and 2013.

